Introduction
In India, where agriculture holds significant value, it directly or indirectly supports the livelihoods of 65% of the population. The agricultural industry’s impact on the country’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is substantial, accounting for approximately 17%. Enhancing this growth factor has become crucial to generate more revenue, income, and employment opportunities. The rapid advancements in technology have brought convenience and progress to various industries, including agriculture. The utilization of drones and Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) has resulted in incremental advancements, saving time and reducing costs.
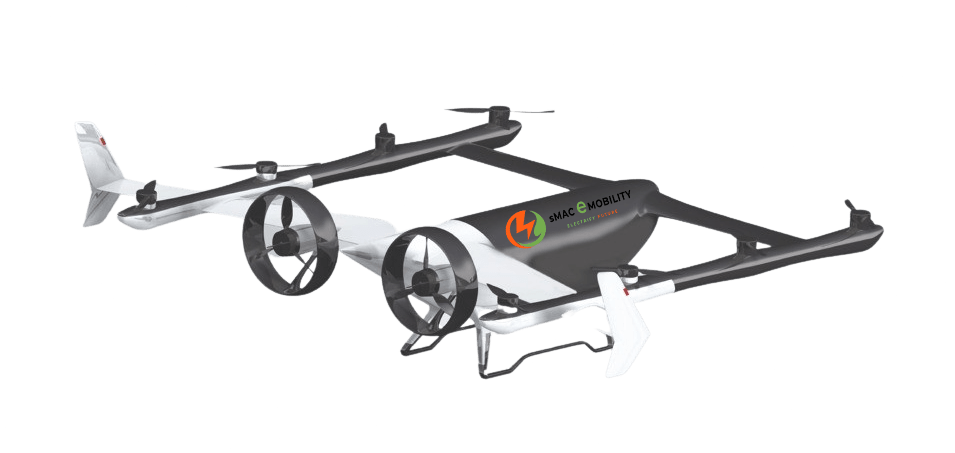
Drones are increasingly being employed in the agricultural sector for a variety of operations, including aerial surveillance, mapping, land inspection, monitoring, fertilization, and identifying diseased or decaying crops, among others. These versatile drones are being tested to determine their most effective applications in agriculture, horticulture, and farming. Quadcopters, with their multi-rotors, prove to be the most favorable option for crop fertilization. On the other hand, fixed-wing drones are suitable for this purpose, although their large structure requires ample space for take-off and landing.
Fertilizer Spraying:

One of the most critical applications of drones in agriculture is their ability to swiftly maneuver and reach designated locations. This flexibility allows drones to spray fertilizers and insecticides, providing crops with essential nutrients. Such measures help maintain the health and well-being of crops, ensuring their growth and vitality. Drone operators have the freedom to monitor the fertilization process, keeping pests, insects, and worms at bay while extending the lifespan of crops.
Soil Health Monitoring:

Drones possess robust capabilities that facilitate the analysis of soil health. Through data collection and processing, UAVs can check, control, and maintain the health and quality of soil. Additionally, drone technology can provide vital nutrients to improve soil health. By employing 3D mapping and data processing, drones efficiently analyze soil health and contribute to its overall enhancement.
Seeding Process:

Agriculture is a demanding and labor-intensive industry that requires skilled labor for various operations. Seeding, in particular, is a time-consuming task that traditionally relies on manual labor. To streamline this process, drone technology is employed to sow seeds across a wide range of crop varieties. Equipped with lasers, sensors, and tanks, drones can quickly and efficiently plant seeds, providing significant assistance in agricultural operations.
Analyzing Deficiencies:

Another remarkable advantage of utilizing drones for crop fertilization is their ability to analyze, identify, and survey crops for any deficiencies. Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras, sensors, and lasers can swiftly perform these operations. Real-time mapping of these deficiencies is also possible, and the collected and processed data can be used to make informed decisions regarding crop management.
Drones for Crop Fertilization:
In conclusion, drones and their applications have significantly alleviated the challenges associated with crop fertilization. Their innovative and potent nature has greatly assisted farmers in their multitude of tasks and operations.